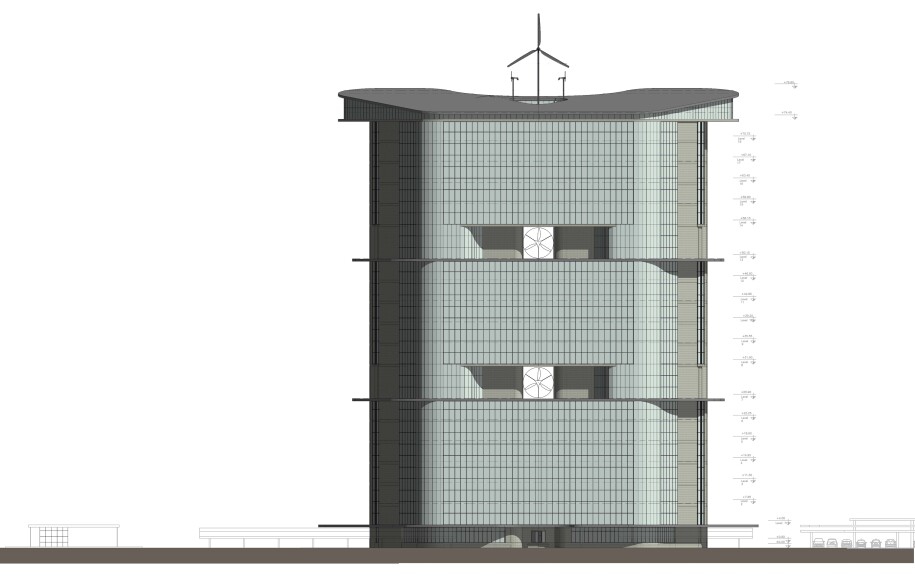
This building can generate clean electricity. The importance of such a building is even more evident in today's low electricity conditions and urban air pollution. We designed our building to use the natural power of the wind, like a ship's sail, and then created corridors in the tower's utility floors that use the enhanced airflow to spin the building's turbines. The design you see has been optimized with calculations and tested with aerodynamic analysis software.
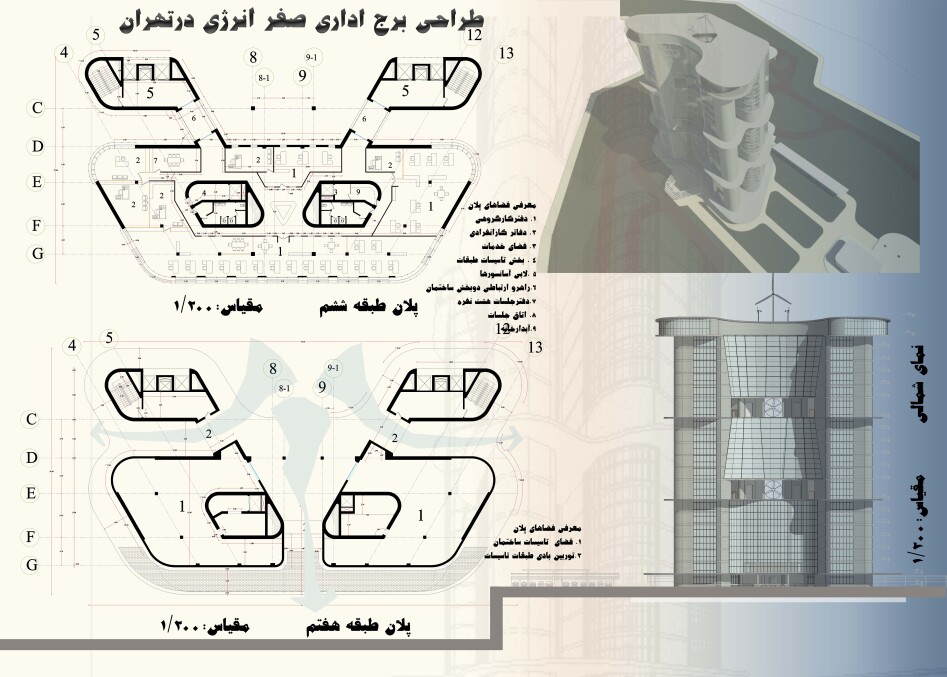
The building consists of three six-story blocks that are stacked on top of each other. Between each block, there is a utility floor, and in these utility floors, three corridors are designed for the passage of air flow and the rotation of the turbines. In the plan of this office tower, we separated the staircases and elevators from the main space of the building into two structural cores. This had four advantages for the design. First, this space no longer needs to be heated and cooled, and energy is not wasted. Second, these two separated structural cores are connected to the main mass with a truss bridge like two super columns, which helps the stability of the tower in earthquakes and strong winds. Third, it allows the building to use wind from all geographical directions to rotate the turbines
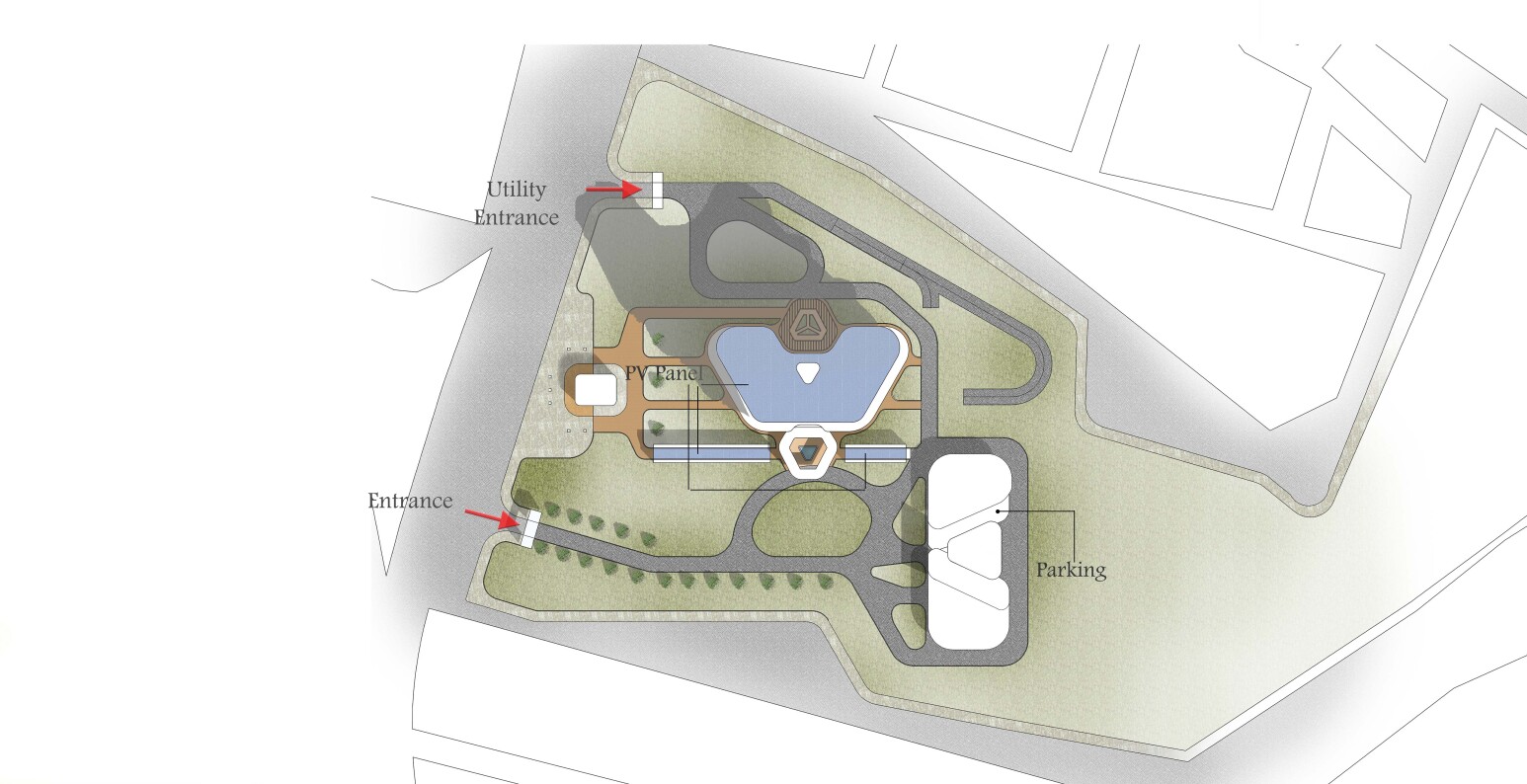
The fourth advantage of separating the structural core of the stairs and elevators from the building is the constructof a large rooftop in the building . Rooftops are one of the best spaces for maximum use of God-given solar energy in the building. We made this roof slightly inclined in the direction of the sun's radiation angle so that if photovoltaic panels or solar absorbers are used, the maximum possible energy can be absorbed and produced
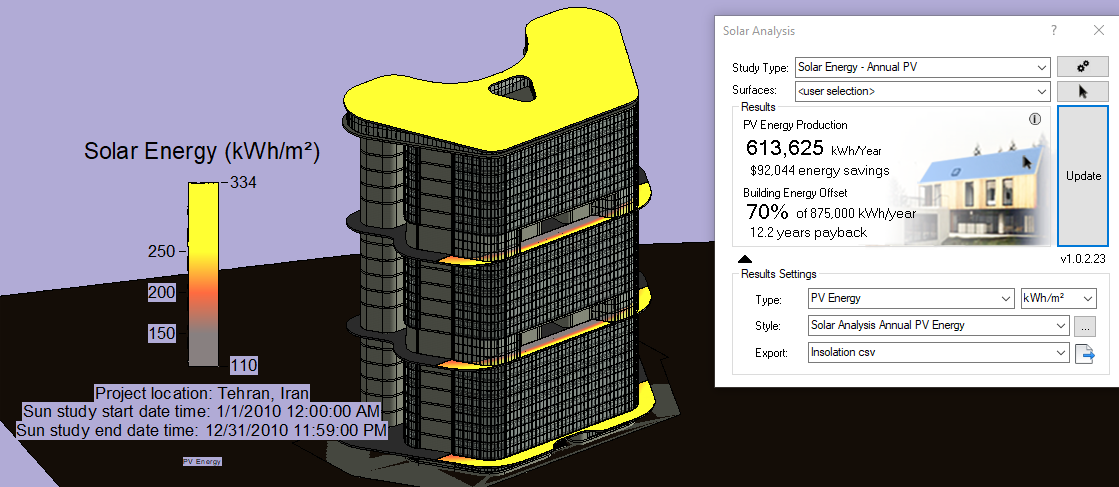
According to our calculations in the Autodesk Revit software, this roof gives us the capacity to produce seventy percent of the building's electricity consumption per year. All these advantages, along with the easy implementation of the project with common structures available in Iran, make this design an excellent option for integrating office units in Tehran

You may be amazing why the main mass is designed in a trapezoid shape. Our studies show that, considering the direction and angle of the sun's radiation in different seasons, the trapezoid mass receives the most heating energy in winter and the least in summer.
In addition, in sustainable buildings, maximum use of the southern facade is very important, so the trapezoid plans were drawn, with the southern facade being three times longer than the eastern and western facades. We installed windows throughout the southern facade that, in addition to providing natural light for employees, also provide natural solar heating in winter.
If window solar collectors are installed, up to ninety-five percent of the building's total heating needs can be met
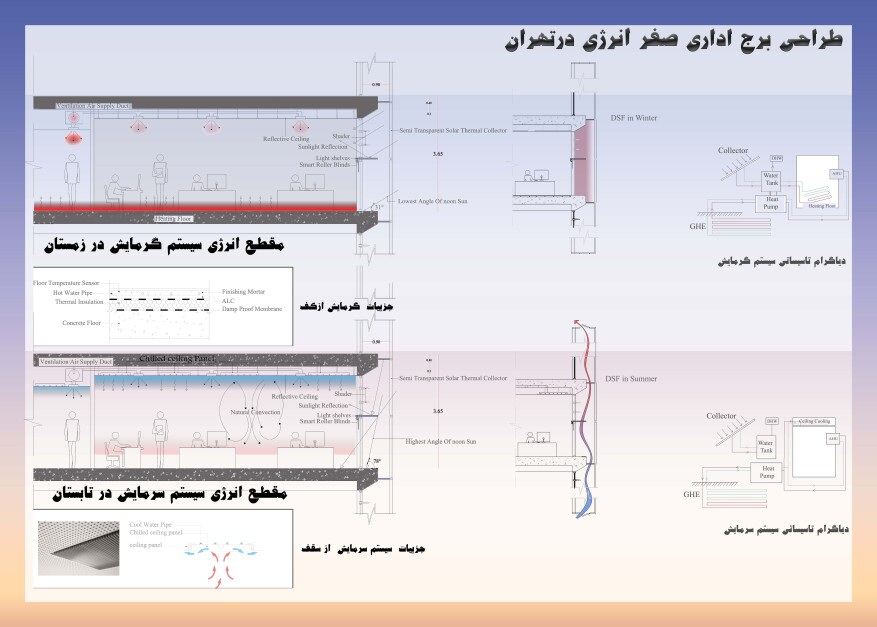
The heating system chosen for this office building was underfloor heating and its cooling system was ceiling cooling.
The reason for choosing these installation systems was to eliminate ductwork and its low depreciation, but the more important point is that the hot coil of this system works at a temperature of forty degrees and its cold coil at a temperature of fifteen degrees!!! This is while we need seventy to eighty degrees to heat the space with a radiator system or fan heater system, which cannot be provided by using solar systems.
In the winter climate of Tehran, solar collectors can easily raise the water temperature to forty degrees even in cloudy weather and provide the underfloor heating system even in critical conditions with the help of a heat pump. In summer, we can also use the underground GHE system, which easily provides us with a temperature of fifteen degrees, and even in critical situations, in combination with a cooling heat pump, it can cool the ceiling by fifteen degrees.

In the design process of this office tower, many issues were examined step by step and the necessary optimizations were made.
For example, aerodynamic analyses of the building mass showed that the airflow through in the corridors of the upper utility floor was decreasing, because the airflow tended to pass over the top of the tower.
Therefore, in the first step, turbines were also considered on the rooftop , and in the second step, at the beginning of the corridor of the upper utility floor, we reached a funnel-shaped entrance to suck more airflow towards itself.
In addition to creating visual appeal, this funnel-shaped section is also considered a transparent and protective double-skin facade in wich provides sound and thermal insulation for tower
One of the optimizations of this zero-energy tower is the appropriate orientation of the building towards the prevailing winds of Tehran's climate.
We obtained climate information from the Tehran weather station and extracted the wind patterns of different seasons of Tehran by using the Climate software. According to this wind pattern information, the prevailing wind direction in Tehran is from the north,
Therefore, the orientation of the building should be such that the air flow in the mass corridors reaches its maximum speed for a longer period of time.
by Using climate analysis, we found the appropriate orientation of the building towards the north wind and with aerodynamic design, we were able to increase the air flow speed in the corridors by three times and make it economical to place the turbine in it.
After designing the construction to maximize energy and electricity production, it is now time to store this energy so that we can sell the excess.
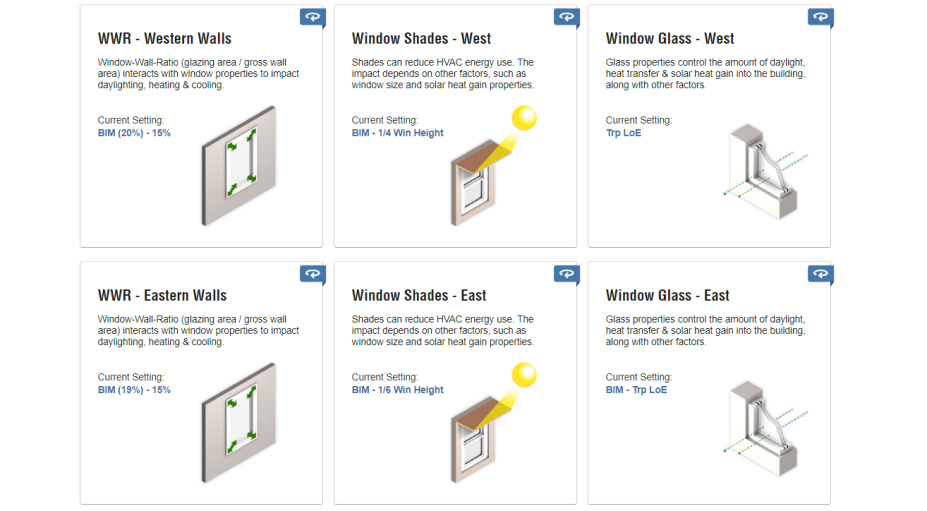
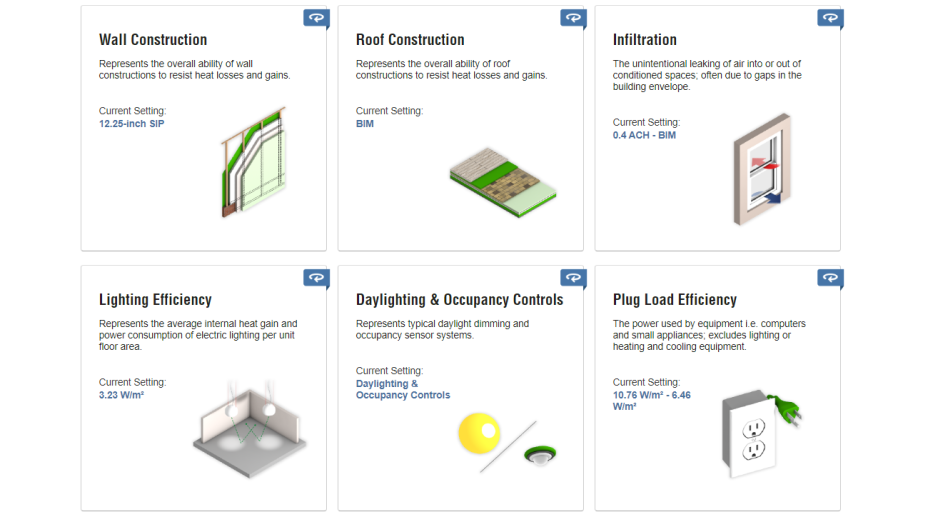
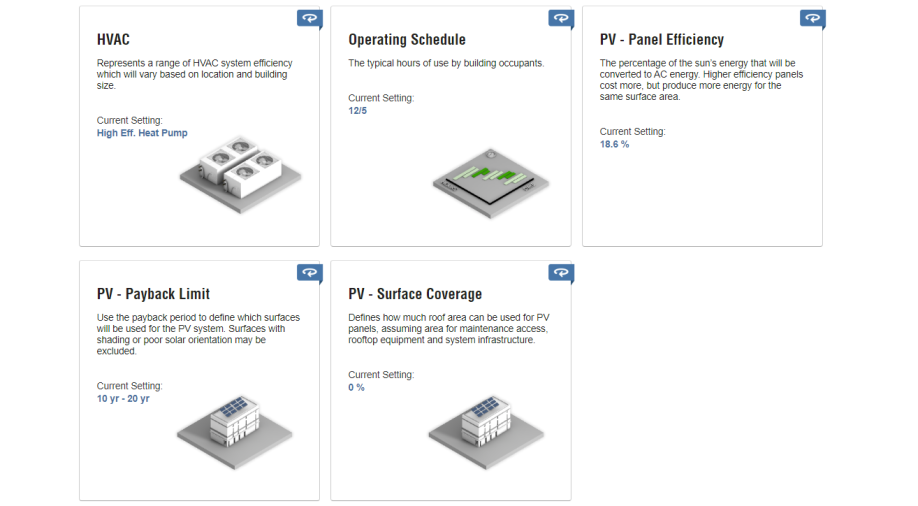
It is very important that energy consumption in such buildings is controlled.
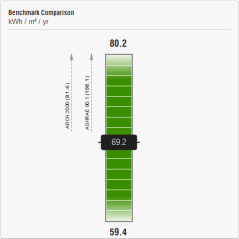
For this, we created a 3D model of the tower in the revit software and uploaded it to the Green Building Studio and Insight 360 websites. By taking and considering the proposed solutions from Autodesk softwares, we optimized the consumption of this building to the point where the energy production in this tower two time the energy consumption.
This means that instead of paying the government an energy bill every month, they should pay you the same amount at the export rate.